Saved scenarios
Those using the ETM web application can save scenarios to their account. These scenarios appear in their saved scenario list. Scenarios in this list are called saved scenarios.
The ETM provides an API for creating, updating, and removing scenarios from your list of saved scenarios.
The SavedScenario object
All scenarios contain the following attributes, which will be part of any response from the scenario endpoint:
id- the numeric id of the saved scenario.scenario_id- the number id of the underlying scenario.area_code- the geographic area which the scenario represents.end_year- the year the scenario ends.title- the title of the saved scenario, shown in the list and when opening the scenario.description- optional long-form text which describes the scenario.scenario_id_history- an array containing up to 20 scenario IDs which represent previous versions of the scenario; see Scenario ID historyprivate- indicates if the saved scenario can only be viewed by its owner (true), or by everyone (false).discarded- whether the saved scenario appears in the trash (true) or the list of saved scenarios (false).created_at- the time at which the saved scenario was created.updated_at– the time when the saved scenario was most recently updated.version- the version associated with the saved scenario. See model versions for more information.scenario- read-only information about the underlying scenario.saved_scenario_users- array about the users associated with the SavedScenario.id- the user's unique ID number.role- the user's role with respect to the SavedScenario.
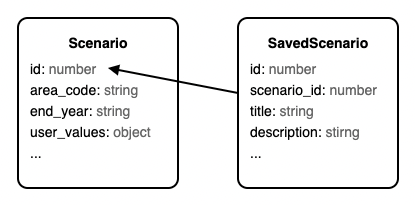
Scenarios vs. saved scenarios
All of the information about the scenarios you create are stored and retrieved as Scenario objects, through the scenarios API. If you use the ETM exclusively through the API, you do not need to use the saved scenarios API. However, if you want a finished scenario to show up in your list of saved scenarios, you will need to also create a saved scenario which references the scenario you created.
Scenario ID history
When the scenario is updated through the web interface, copies of the previous version of the scenario will be saved and added to the scenario_id_history list, and the scenario_id will be updated to point to a new scenario.
This list cannot be modified through the API, nor do changed to the underlying scenario through the API cause new versions to be added to this list.
Getting information about a saved scenario
Fetch information about a saved scenario. This will include a copy of the information about the underlying scenario.
- Endpoint
- GET /api/v3/saved_scenarios/{id}
- Path parameters
idnumberthe ID of the saved scenario
- Token
This endpoint requires an authentication token with at least the following scopes:
scenarios:readRead your public and private scenarios
GET /api/v3/saved_scenario/123 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 456789,
"scenario_id_history": [
456788
],
"title": "My saved scenario",
"area_code": "nl2019",
"end_year": 2050,
"private": false,
"discarded_at": false,
"created_at": "2022-07-27T13:45:32.000Z",
"updated_at": "2022-12-22T19:21:32.000Z",
"version": "latest",
"saved_scenario_users": [
{
"user_id": 123,
"role": "scenario_owner"
}
],
"scenario": {
"id": 456789,
"created_at": "2022-07-27T15:59:33.000Z",
"updated_at": "2022-12-20T17:47:41.000Z",
"user_values": {
"households_number_of_inhabitants": 19.5,
"households_useful_demand_for_cooling": 2.5
},
"end_year": 2050,
"keep_compatible": true,
"private": false,
"area_code": "nl2019",
"source": "ETM",
"balanced_values": {},
"metadata": {},
"active_couplings": [],
"start_year": 2019,
"inactive_couplings": [],
"scaling": null,
"template": 123456,
"url": "https://engine.energytransitionmodel.com/api/v3/scenarios/456789"
}
}
Listing your saved scenarios
You can get a list of all saved scenarios which belong to you. The list is paginated.
- Endpoint
- GET /api/v3/saved_scenarios
- Path parameters
pagenumberthe page number to fetchlimitnumberthe number of items per page
- Token
This endpoint requires an authentication token with at least the following scopes:
scenarios:readRead your public and private scenarios
GET /api/v3/saved_scenarios HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"links": {
"first": "https://engine.energytransitionmodel.com/api/v3/saved_scenarios?page=1",
"prev": null,
"next": "https://engine.energytransitionmodel.com/api/v3/saved_scenarios?page=2",
"last": "https://engine.energytransitionmodel.com/api/v3/saved_scenarios?page=3"
},
"meta": {
"limit": 25,
"count": 25,
"total": 65,
"current_page": 1,
"total_pages": 3
},
"data": [
{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 456789,
"scenario_id_history": [
456788
],
"title": "My saved scenario",
"description": null,
"area_code": "nl2019",
"end_year": 2050,
// ...
},
// ...
]
}
Create a saved scenario
Creating a saved scenario will cause it to appear in your list of saved scenarios in the web application.
- Endpoint
- POST /api/v3/saved_scenarios
- Parameters
scenario_idintegerRequiredthe ID of the underlying scenario (required)titlestringRequiredwhat to call the saved scenario (required)descriptionstringan optional description for the saved scenarioprivatebooleanwhether the scenario can be viewed only by the owner
- Token
This endpoint requires an authentication token with at least the following scopes:
scenarios:readRead your public and private scenarios
scenarios:writeCreate and update your public and private scenarios
Before you can create a saved scenario, you must create the underlying scenario. The response will include the ID number of your new scenario. You may then create a saved scenario as a second step, passing the scenario ID:
POST /api/v3/saved_scenarios HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"scenario_id": 12345,
"title": "My saved scenario"
}
{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 12345,
"scenario_id_history": [],
"title": "My saved scenario",
"description": null,
"area_code": "nl2019",
"end_year": 2050,
"private": false,
"discarded": false,
"created_at": "2022-12-23T19:21:32.000Z",
"updated_at": "2022-12-23T19:21:32.000Z",
"saved_scenario_users": [
{
"id": 123,
"role": "scenario_owner"
}
],
"scenario": {
"id": 12345,
// ...
}
}
Update a saved scenario
Update a saved scenario by assigning a new underlying scenario, title, or description.
- Endpoint
- PUT /api/v3/saved_scenarios/{id}
- Path parameters
idnumberthe ID of the saved scenario
- Parameters
scenario_idintegerthe ID of the underlying scenario (required)titlestringwhat to call the saved scenario (required)descriptionstringan optional description for the saved scenarioprivatebooleanwhether the scenario can be viewed only by the ownerdiscardedbooleanwhether the scenario should be in the owner's trash
- Token
This endpoint requires an authentication token with at least the following scopes:
scenarios:readRead your public and private scenarios
scenarios:writeCreate and update your public and private scenarios
PUT /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"title": "A new title",
"scenario_id": 67890
}
{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 67890,
"scenario_id_history": [12345],
"title": "A new title",
"description": null,
"area_code": "nl2019",
"end_year": 2050,
"private": false,
"discarded": false,
"created_at": "2022-12-23T19:21:32.000Z",
"updated_at": "2022-12-23T19:22:38.000Z",
"saved_scenario_users": [
{
"id": 123,
"role": "scenario_owner"
}
],
"scenario": {
"id": 67890,
// ...
}
}
Managing saved scenario users
Saved scenarios support collaborative access through user management. You can invite other users to view or edit your saved scenarios by granting them specific roles.
User changes propagate asynchronously to all historical versions of the saved scenario.
Batch requests
All user management operations can be performed in batches: adding, updating, or removing multiple users in one request. The response will contain a JSON array of successfully processed users. When one or more users fail, the response will be 422 and contain the following:
success- The users that were successfully processed.errors- The users that were not successful, with error details.
This partial success behavior ensures that valid operations are persisted even when some fail, allowing you to see exactly which users succeeded and which failed.
User roles
There are three roles available for saved scenario users:
- scenario_owner - Full control over the scenario, including the ability to manage users, edit settings, and delete the saved scenario
- scenario_collaborator - Can view and edit the scenario, but cannot manage users or delete the saved scenario
- scenario_viewer - Read-only access to view the scenario
Every saved scenario must have at least one owner. The API will prevent you from removing the last owner.
See also the saved scenario access page for more information.
Listing users on a saved scenario
Retrieve all users associated with a saved scenario:
GET /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123/users HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
[
{
"id": 1,
"user_id": 456,
"user_email": null,
"role": "scenario_owner",
"role_id": 0,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
},
{
"id": 2,
"user_id": null,
"user_email": "collaborator@example.com",
"role": "scenario_collaborator",
"role_id": 1,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
}
]
Adding users to a saved scenario
Add one or more users to a saved scenario. Users can be identified by email address, and will receive an invitation to access the scenario.
All user management endpoints support bulk operations. You can add, update, or remove multiple users in a single request by providing an array of user objects.
POST /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123/users HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"saved_scenario_users": [
{
"user_email": "viewer@example.com",
"role": "scenario_viewer"
},
{
"user_email": "collaborator@example.com",
"role": "scenario_collaborator"
}
]
}
[
{
"id": 3,
"user_id": null,
"user_email": "viewer@example.com",
"role": "scenario_viewer",
"role_id": 3,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
},
{
"id": 4,
"user_id": null,
"user_email": "collaborator@example.com",
"role": "scenario_collaborator",
"role_id": 1,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
}
]
If a user with the provided email address already has an ETM account, they will be automatically coupled when added (the user_id will be populated). Otherwise, they will receive an invitation email.
Updating user roles
Change the role of one or more users. Users can be identified by user_id, user_email, or the SavedScenarioUser id.
PUT /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123/users HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"saved_scenario_users": [
{
"user_email": "viewer@example.com",
"role": "scenario_collaborator"
}
]
}
[
{
"id": 3,
"user_id": null,
"user_email": "viewer@example.com",
"role": "scenario_collaborator",
"role_id": 1,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
}
]
Removing users from a saved scenario
Remove one or more users from a saved scenario. Users can be identified by user_id, user_email, or the SavedScenarioUser id.
DELETE /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123/users HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"saved_scenario_users": [
{
"user_email": "viewer@example.com"
}
]
}
The API will return a 204 No Content response on success.
You cannot remove the last owner from a saved scenario. The API will return a 422 Unprocessable Entity error if you attempt to do so.
Error handling
User management operations support partial success:
- Each user in a bulk request is processed independently
- Successfully processed users are saved to the database
- Failed users are reported in the error response
- The API returns a
422 Unprocessable Entitystatus when any user fails - The response includes both successful users and errors
{
"success": [
{
"id": 3,
"user_id": null,
"user_email": "viewer@example.com",
"role": "scenario_viewer",
"role_id": 3,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
},
{
"id": 4,
"user_id": 789,
"user_email": null,
"role": "scenario_collaborator",
"role_id": 1,
"saved_scenario_id": 123
}
],
"errors": {
"invalid@example.com": ["role_id"],
"duplicate@example.com": ["duplicate"]
}
}
When a bulk operation returns partial success, the successful changes are persisted to the database. Only the failed operations need to be retried.
Common errors include:
duplicate- User is already associated with the saved scenariorole_id- Invalid role specifiednot_found- User not found when updating or removingownership- Cannot remove or change the last owner
For managing users on regular scenarios (not saved scenarios), see Scenario Users.
Update the underlying scenario
As described in scenarios vs. saved scenarios, a saved scenario is just a way to keep track of a scenario. It allows you to show it in your list of saved scenarios in the ETM web application. You cannot directly change the underlying scenario through the saved scenario.
However, the saved scenario does provide you with the ID of the scenario object, and with that you can perform any action you wish. See the documentation for the scenario API for more information.
There are two approaches to updating the scenario itself:
Update the scenario directly
Fetch the saved scenario
Start by fetching the details of the saved scenario. much of the information in the reply is not relevant when updating the scenario; we care only about the returned
scenario_id.RequestGET /api/v3/saved_scenario/123 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKENResponse{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 456789,
"scenario_id_history": [],
"title": "My saved scenario",
"description": null,
// ...
}Update the scenario using the scenario ID.
Send a request to the API to update the scenario with whatever new values you want. You can also perform queries, get CSVs, or perform any other scenario action with the scenario ID. The above response returns a scenario ID of
456789so we'll use that in the example below.RequestPUT /api/v3/scenarios/456789 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"scenario": {
"user_values": {
"buildings_insulation_level": 35.7
}
}
}
Your scenario has now been updated with the new user_value settings.
This approach can be used for any action that you would normally perform on a scenario: fetch the saved scenario to get the scenario_id, then perform an action on the scenario. For example, to download the electricity price curve CSV, fetch the saved scenario, then perform a GET request on the scenario's CSV endpoint:
curl https://engine.energytransitionmodel.com/api/v3/scenarios/456789/curves/electricity_price.csv \
-H "Accept: text/csv" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN"
Clone the scenario and update the saved scenario
An alternative to updating the scenario directly, is to create a clone of the scenario, modify that, then change the saved scenario to point to the new scenario.
This has the advantage of preserving the original scenario, and the saved scenario will track the most recent 20 scenarios used. This allows you to maintain a simple history of the changes you've made to the scenario.
Fetch the saved scenario
As before, we start by fetching the details of the saved scenario in order to get the
scenario_id.RequestGET /api/v3/saved_scenario/123 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKENResponse{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 123456,
"scenario_id_history": [],
"title": "My saved scenario",
"description": null,
// ...
}The returned
scenario_idis123456.Clone the scenario
Clone the scenario using the scenario ID. This will create a new scenario with the same settings as the original scenario.
RequestPOST /api/v3/scenarios HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"scenario": {
"scenario_id": "123456"
}
}Response{
"id": 123457,
"area_code":"nl",
"start_year": 2019,
"end_year": 2050,
"user_values": {
"buildings_insulation_level": 35.7
}
// ...
}The API returns details of the new scenario, including the new scenario ID. In this example, the new scenario ID is
123457.Update the scenario
We'll now send a request to the API to update the scenario with whatever new values you want.
RequestPUT /api/v3/scenarios/123457 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"scenario": {
"user_values": {
"buildings_insulation_level": 42.0,
"households_number_of_inhabitants": 18.3,
"households_solar_pv_solar_radiation_market_penetration": 21.0
}
}
}Update the saved scenario
Finally, we'll update the saved scenario to point to the new scenario. This is done by sending a request to the API to update the saved scenario with the new scenario ID.
RequestPUT /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN
{
"scenario_id": 123457
}Response{
"id": 123,
"scenario_id": 123457,
"scenario_id_history": [123456],
"title": "My saved scenario",
"description": null,
// ...
}The saved scenario now points at your new scenario, and the the original scenario is preserved in the
scenario_id_history.
Delete a saved scenario
Saved scenarios may also be permanently deleted. This actions skips moving the saved scenario to the trash and deletes it immediately.
Deleting a saved scenario removes it from your list of saved scenarios in the web application. It does not delete the underlying scenario. You may delete scenarios owned by your account as a separate action; see Deleting your scenarios.
- Endpoint
- DELETE /api/v3/saved_scenarios/{id}
- Path parameters
idnumberthe ID of the saved scenario
- Token
This endpoint requires an authentication token with at least the following scopes:
scenarios:readRead your public and private scenarios
scenarios:deleteDelete your public and private scenarios
DELETE /api/v3/saved_scenarios/123 HTTP/2
Host: engine.energytransitionmodel.com
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_TOKEN